Agnostic of networking technology, cloud provider or telecommunication carrier we provide secure connectivity as a Service to any location in the world. Using the most advanced connectivity platform, ngena accelerates cloud transformation, improves cyber-security and enables enterprise digitalization at low cost and high speed
Download Company Overview
At ngena, we believe that digitization is the driving force of the new economy, and that automation and managed services are the most efficient, cost effective and future-proof route to enable enterprises to enter the global and flexible economy enabled by digital transformation.
Digital transformation allows enterprises of any size to operate globally and, at the same time, have the best enabling technology immediately available through the cloud. Enjoying the full potential of this cloud-based economy is predicated upon ubiquitous connectivity that is both reliable and cost effective.
Remote workforce is a key asset to enterprises, both to leverage the best talents wherever they are, and to be resilient to disruptions. Guaranteeing the same employee experience whether your employees are at office, at home or on the road is key to enable everyone to contribute at their best, wherever they are.

While intellectual property is increasingly dispersed over the cloud or roaming laptops, some industries need to retain a significant amount of centralized information. Security must be effective whether the data are on-prem or in the cloud, at rest or in motion, tailoring itself to the nature of each specific business.

Your evolution from classical IT into the digitized world requires evolving your connectivity and security infrastructure
To get the best out of the new technology and to take advantage of best-in-class technology providers. This evolution means reshaping your operations to deal with a completely new operating paradigm and needs to happen quickly to beat competition, nimbly to keep pace with your business needs, and with a cost model that supports your business and helps you achieve your financial targets.
Global reach everywhere your enterprise needs it. In addition ngena is introducing new cloud HUBs
Colleagues
Partners
Data hubs
Backbone miles
In this complex context, ngena brings clarity and efficiency, marrying apparently irreconcilable aspects like global reach and local care, reusable components and bespoke solutions, sophisticated technology and user-friendly experience, to enable our partners to focus on their enterprise customers needs
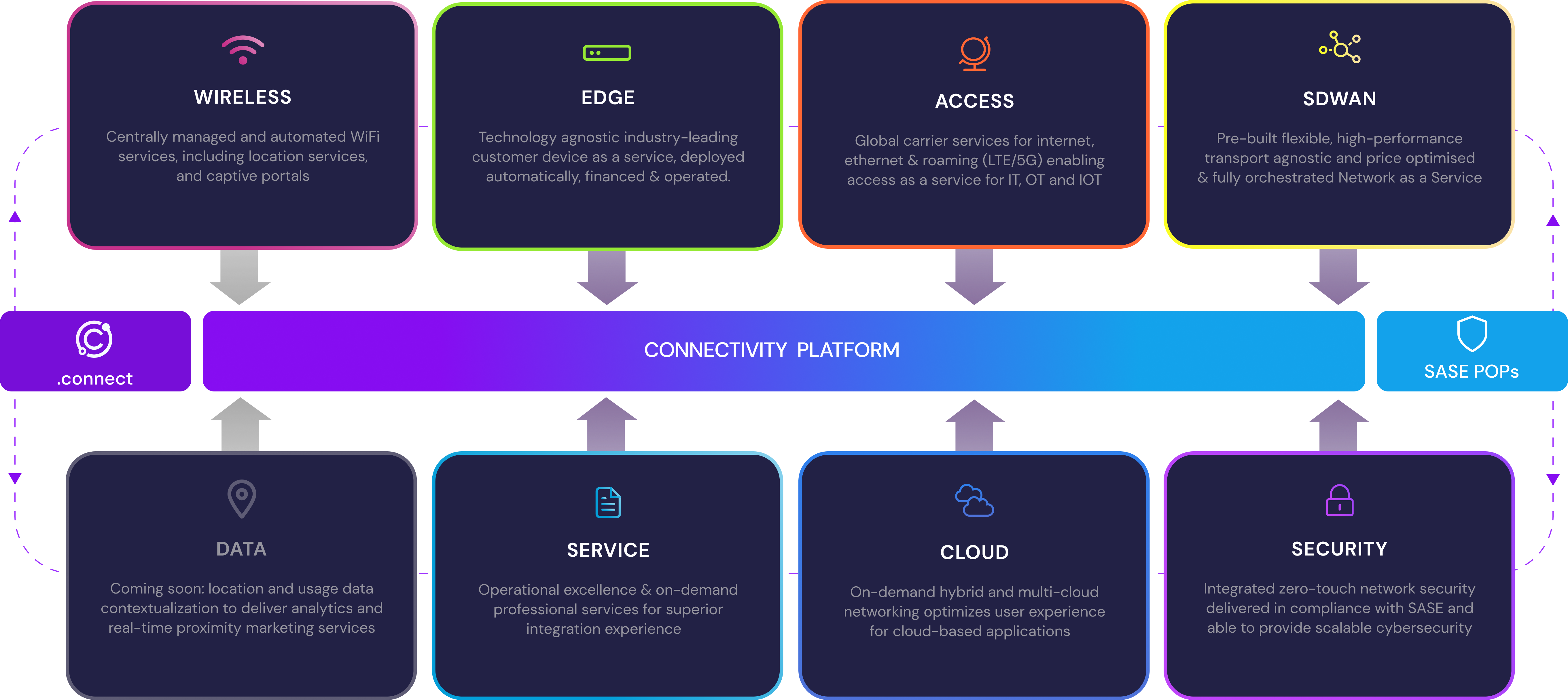
The 7 pillars of our portfolio provide a pragmatical and intuitive view of the different capabilities digitization deals with, all offered as-a-service:
Edge
Industry-leading WAN edge in an “as a Service” model, deployed, financed and managed by ngena in more than 200 countries
SD-WAN
Flexible, high-performance, transport agnostic and price optimized, fully orchestrated NaaS with pre-designed access solutions suitable for roaming users and small branches up to datacenters
Cloud
Multiple cloud access options and native cloud networking optimize user experience for cloud-based applications
Access
A global alliance of carrier providers enable last and first mile as true Access as a Service in more than 200 countries
Security
Enabling SASE by deploying security at the WAN Edge, the Cloud edge or the ngena SASE POP via leading Cloud Security Providers
Service
Operational excellence for our Managed Services offerings and on-demand professional services for superior integration experience
Behind the scenes, a global team of professionals and an infrastructure that spans across continents is comprised of private backbone connectivity, distributed infrastructure for orchestration and Continuous Delivery. SASE enabled Points of Presence (co-located with major Public Cloud Providers) enable our customers to leverage the full potential of the best that technology has to offer in a full service fashion.
Our integrated ecosystem of partners allows us to increase speed, simplicity and security when providing connectivity to our valued customers. Innovation and reliability are key to our more than 60 partners around the globe so they can provide local implementation.

While intellectual property is increasingly dispersed over the cloud or roaming laptops, some industries need to retain a significant amount of centralized information.



The Challenge
Your data connectivity network is the backbone of your global business and critical to the success of your company. You need a trustworthy and reliable partner who has proven skills and a longstanding track record to guarantee the highest quality for all your network services, including world-class security and service levels agreements. Now you might be asking yourself whether a market entrant and innovator, such as ngena, is really a good choice for you.
The Solution
With ngena, you will be working with the world’s best telecommunication operators and technology suppliers: 50+ telecommunication service providers and system integrators – among them many incumbents and market leaders – will give you access to their global SASE & Software-Defined Wide Area Networks (SD-WAN) via ngena’s global technology platform and backbone to almost any part of the world. The platform we have built is based on proven technologies from Cisco/Viptela, Zscaler, Equinix, ServiceNow and many more, and is therefore completely reliable and industry proven. Your local operator will be your single point of contact and offer you a comprehensive set of enterprise-grade services, business-oriented Service Level Agreements, and world-class service assurance. Already more than 50 enterprises are running key parts of their networks on ngena’s platform.
The Challenge
Your data connectivity network is the backbone of your global business and critical to the success of your company. You need a trustworthy and reliable partner who has proven skills and a longstanding track record to guarantee the highest quality for all your network services, including world-class security and service levels agreements. Now you might be asking yourself whether a market entrant and innovator, such as ngena, is really a good choice for you.
The Solution
With ngena, you will be working with the world’s best telecommunication operators and technology suppliers: 50+ telecommunication service providers and system integrators – among them many incumbents and market leaders – will give you access to their global SASE & Software-Defined Wide Area Networks (SD-WAN) via ngena’s global technology platform and backbone to almost any part of the world. The platform we have built is based on proven technologies from Cisco/Viptela, Zscaler, Equinix, ServiceNow and many more, and is therefore completely reliable and industry proven. Your local operator will be your single point of contact and offer you a comprehensive set of enterprise-grade services, business-oriented Service Level Agreements, and world-class service assurance. Already more than 50 enterprises are running key parts of their networks on ngena’s platform.
The Challenge
According to recent surveys, 41% of businesses globally say they do business in countries outside their own. This means that, at many companies, network operations must be seen as a global task. Unfortunately, however, setting up, managing and monitoring global networks 24/7 still remains highly complex. This also implies that many members of your IT department are tied up with time-consuming activities such as multi-provider management and incident resolution. In addition, the complexity of global networks traditionally leads to a very slow roll-out of new sites, and limited flexibility in implementing change requests and network optimizations.
The Solution
The ngena Secure Connectivity as a Service was developed to cope with these requirements. It offers you a global SASE & SD-WAN from a single source – your trusted local provider that is a member of the ngena partner ecosystem. This is possible because ngena has formed an ecosystem of 30+ leading telecommunication providers that offer their Ethernet and Internet access in around 200 territories worldwide to give your company truly global connectivity. Along with the strength of the global ecosystem comes the power of a global platform and the .connect with a central portal that enables ngena ecosystem partners to design, order, set-up, monitor and maintain global SD-WANs with a click of a mouse. The use of innovative abstraction, virtualisation and a data- & model-driven end-to-end orchestration now allows global enterprise networks to be rolled out more quickly, and with greater flexibility to change or upgrade services in response to prevailing business needs.
